REST | API | HTTP | JSON
REST (Representational State Transfer) is a software architectural style that defines a set of constraints for creating web services. REST is used to create web services that are lightweight, maintainable, and scalable.
REST is based on the idea of representing the state of a resource, such as a document or database record, using a simple and predictable set of operations such as GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE. These operations are called HTTP methods and correspond to the four basic CRUD operations (create, read, update, delete) commonly used in database systems.
REST is used to create APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) that allow different software systems to communicate with each other over the Internet. REST APIs use the HTTP protocol, which is the foundation of the World Wide Web, to send and receive data.
Some technologies related to REST are:
JSON (JavaScript Object Notation): A lightweight data exchange format commonly used in REST APIs to send data between the client and the server.
OAuth (Open Authorization): An open standard for authorization that allows users to share their private resources (such as photos, videos, and documents) stored on one website with another without sharing their credentials.
Swagger: A tool for creating and documenting REST APIs. Swagger allows developers to describe the structure of their APIs in a standardized format and create interactive documentation, client libraries, and server stubs.
Overall, REST is a widely used approach to building APIs and is an important part of the modern web.
BITS experts have used REST in a variety of projects. A selection of case studies and references can be found below.
“We are happy to support you with your digital challenges and look forward to hearing from you without obligation.”
Marc Schallehn, Managing Director BITS GmbH

Gerne unterstützen wir Sie bei Ihren IT Projekten. Ich freue mich über Ihre Kontaktaufnahme.
Selection of case studies and references
Regulatory affairs under control – a digital solution for international requirements and compliance processes
BITS implemented a digital platform for the structured management of international regulations - for greater transparency and secure compliance processes.
Data management
Data management Your data, your success - efficient data management with BITS In today's data-driven business world, efficient and well thought-out data management is the key to success. BITS GmbH supports companies in [...]
Programming, operation and further development of the curated recruiting platform swarmscout.com for personal network recruiting
On behalf of opexxia GmbH, a consulting and implementation agency for complex operational projects in the retail sector, BITS GmbH as IT development partner implemented and successfully put into operation the Internet recruiting platform swarmscout.com.
Integration of GPT-4 (ChatGPT) via OpenAI API into an enterprise travel application for automated curated content generation.
The goal of this project was to streamline the process of creating personalized recommendations for places and experiences through the use of artificial intelligence (AI) by integrating features of GPT-4 (ChatGPT) into an enterprise web app via the OpenAI API.
New and further development of a B2B software for order processing in the automotive sector
The goal of this project was to update a B2B software of a leading European vehicle manufacturer to the latest technical state of the art. Thus, not only the security level should be increased, but also the usability should be optimized. Furthermore, additional business processes and functionalities were added to the software.
Development of a web application and a mobile app to improve breast cancer patient follow-up.
Together with Apps in Medicine GmbH, AOK Bayern, DAK Gesundheit and Siemens Betriebskrankenkasse (SBK), under the direction of the Klinikum rechts der Isar of the Technical University of Munich (MRI), BITS participated in the PRISMA study as a consortium partner for the technical infrastructure.
Establishment and operation of a European trading platform for pharmaceuticals
Together with arex PHARMA GmbH, a specialist in the international trade and distribution of European pharmaceuticals, BITS GmbH has established the EU-wide trading platform Rxchange for pharmaceutical products as a strategic IT partner.
Development of a web application for automated exchange of information between partner brands
A web application developed by BITS was expanded to include a Group-wide shortage management process.
Internationalization of an application in particular of the function extension for 21 ESA markets as well as for importers
Further development of a Java business application of vehicle service contracts for international use.
Connection of production machines of a medium-sized manufacturer to the Industry 4.0 OEE solution of BITS for monitoring and optimization of production
In this Industry 4.0 project, BITS' task was to monitor and control production machines with the help of an OEE solution in order to optimize quality, capacity utilization and costs.
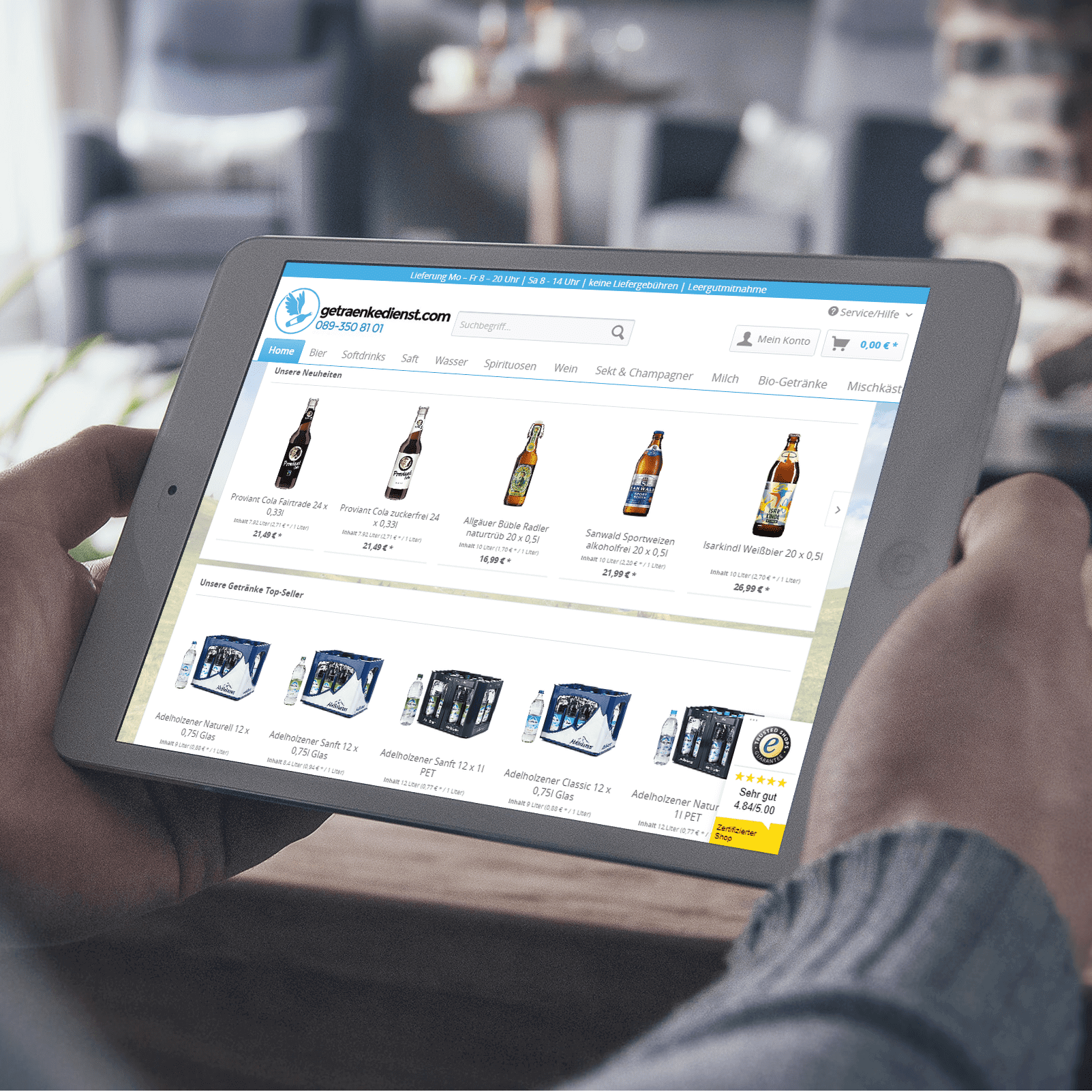
Development and operation of the DACH wide Internet e-commerce platform www.getraenkedienst.com
Together with drink now GmbH, a specialist in beverage sales, BITS GmbH has set up and operates the Internet e-commerce platform www.getraenkedienst.com as a strategic IT partner successful to this day.
Realization of MVPs
BITS has realized a large number of MVPs, prototypes or proof of conctepts. The central goal here is to test a new idea, an alternative orientation or an improvement with the least possible effort and, if successful, to expand it further.
Hospitality Solutions
We are happy to advise you in the areas of Property Management Systems apaleo/Micros/Oracle Opera and Hospitality IT Solutions. Together with our partners, we support you with customice in the implementation of integrated sales solutions for meetings, incentives and events on your hotel website.
Fullstack web development
Fullstack web development is one of our core competencies and has been practiced by our staff for over 25 years. Besides the excellent expert knowledge in backend and frontend development of normal or highly complex web applications, we are also specialized in all related technologies, processes and methods as well as architecture and operation of web applications up to high availability.