HTML
HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) is a standardized programming language used to create web pages and web applications. It allows describing the structure and content of a web document so that browsers can display the content correctly for users.
HTML can be used to define the various elements of a web page, such as headings, paragraphs, lists, and links. The <p> tag is used to define a paragraph, while the <h1> tag defines a first-level heading. You can also add images, videos and other multimedia content to the website. Also, HTML can be used to create forms that allow users to enter and submit data to the website.
Besides HTML, there are a number of other technologies for creating web pages and applications. These include:
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets): CSS is used to define the visual style of a web page, including colors, fonts, and layout. It allows web developers to separate the content of a web page (written in HTML) from its presentation (defined in CSS), making it easier to maintain and update the appearance of a website.
JavaScript: JavaScript is a programming language commonly used to add interactivity to web pages. It enables web developers to create dynamic, user-friendly interfaces that can update and change in response to user input.
DOM (Document Object Model): The DOM is a tree-like representation of a web page that is created by a browser when a web page is loaded. It allows web developers to manipulate the content and structure of a web page programmatically using JavaScript.
Together, these technologies form the foundation for creating modern, interactive websites and web applications.
BITS experts have used HTML as well as other programming languages in a variety of projects. A selection of case studies and references can be found below.
“We are happy to support you with your digital challenges and look forward to hearing from you without obligation.”
Marc Schallehn, Managing Director BITS GmbH

Gerne unterstützen wir Sie bei Ihren IT Projekten. Ich freue mich über Ihre Kontaktaufnahme.
Selection of case studies and references
Regulatory affairs under control – a digital solution for international requirements and compliance processes
BITS implemented a digital platform for the structured management of international regulations - for greater transparency and secure compliance processes.
Digitalization where the data is generated – efficient mobile data acquisition for precise vehicle testing
BITS has digitized the vehicle testing process with a mobile solution specially developed for field use - efficient, offline-capable and perfectly integrated into existing systems.
Software development
Software development The perfect solution for your requirements - customized software from BITS In a digitalized world, it is crucial to use software solutions that are not only powerful, but also precisely tailored [...]
New and further development of a B2B software for order processing in the automotive sector
The goal of this project was to update a B2B software of a leading European vehicle manufacturer to the latest technical state of the art. Thus, not only the security level should be increased, but also the usability should be optimized. Furthermore, additional business processes and functionalities were added to the software.
Development of a web application and a mobile app to improve breast cancer patient follow-up.
Together with Apps in Medicine GmbH, AOK Bayern, DAK Gesundheit and Siemens Betriebskrankenkasse (SBK), under the direction of the Klinikum rechts der Isar of the Technical University of Munich (MRI), BITS participated in the PRISMA study as a consortium partner for the technical infrastructure.
Development of individual software for companies
Development of individual software for companies Custom Software We would like you to perceive us as a partner who stands by you in all questions concerning your software projects. We strive to [...]
Supporting an automotive manufacturer with end-of-support migration
On-schedule service migration with the support of BITS in the areas of IT project management and IT consulting
Development of a web application for automated exchange of information between partner brands
A web application developed by BITS was expanded to include a Group-wide shortage management process.
Internationalization of an application in particular of the function extension for 21 ESA markets as well as for importers
Further development of a Java business application of vehicle service contracts for international use.
Connection of production machines of a medium-sized manufacturer to the Industry 4.0 OEE solution of BITS for monitoring and optimization of production
In this Industry 4.0 project, BITS' task was to monitor and control production machines with the help of an OEE solution in order to optimize quality, capacity utilization and costs.
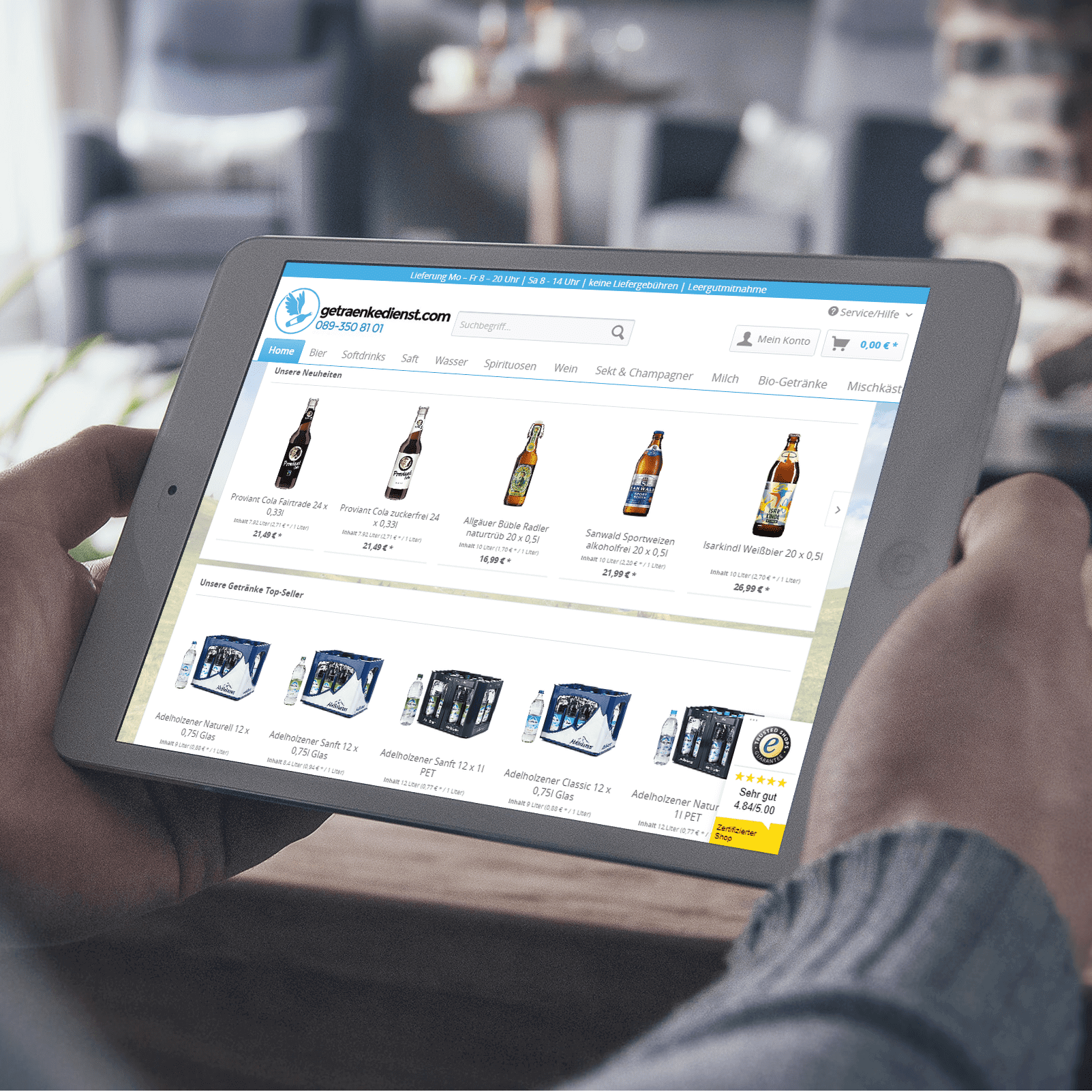
Development and operation of the DACH wide Internet e-commerce platform www.getraenkedienst.com
Together with drink now GmbH, a specialist in beverage sales, BITS GmbH has set up and operates the Internet e-commerce platform www.getraenkedienst.com as a strategic IT partner successful to this day.
Realization of MVPs
BITS has realized a large number of MVPs, prototypes or proof of conctepts. The central goal here is to test a new idea, an alternative orientation or an improvement with the least possible effort and, if successful, to expand it further.